DIABETES MELLITUS
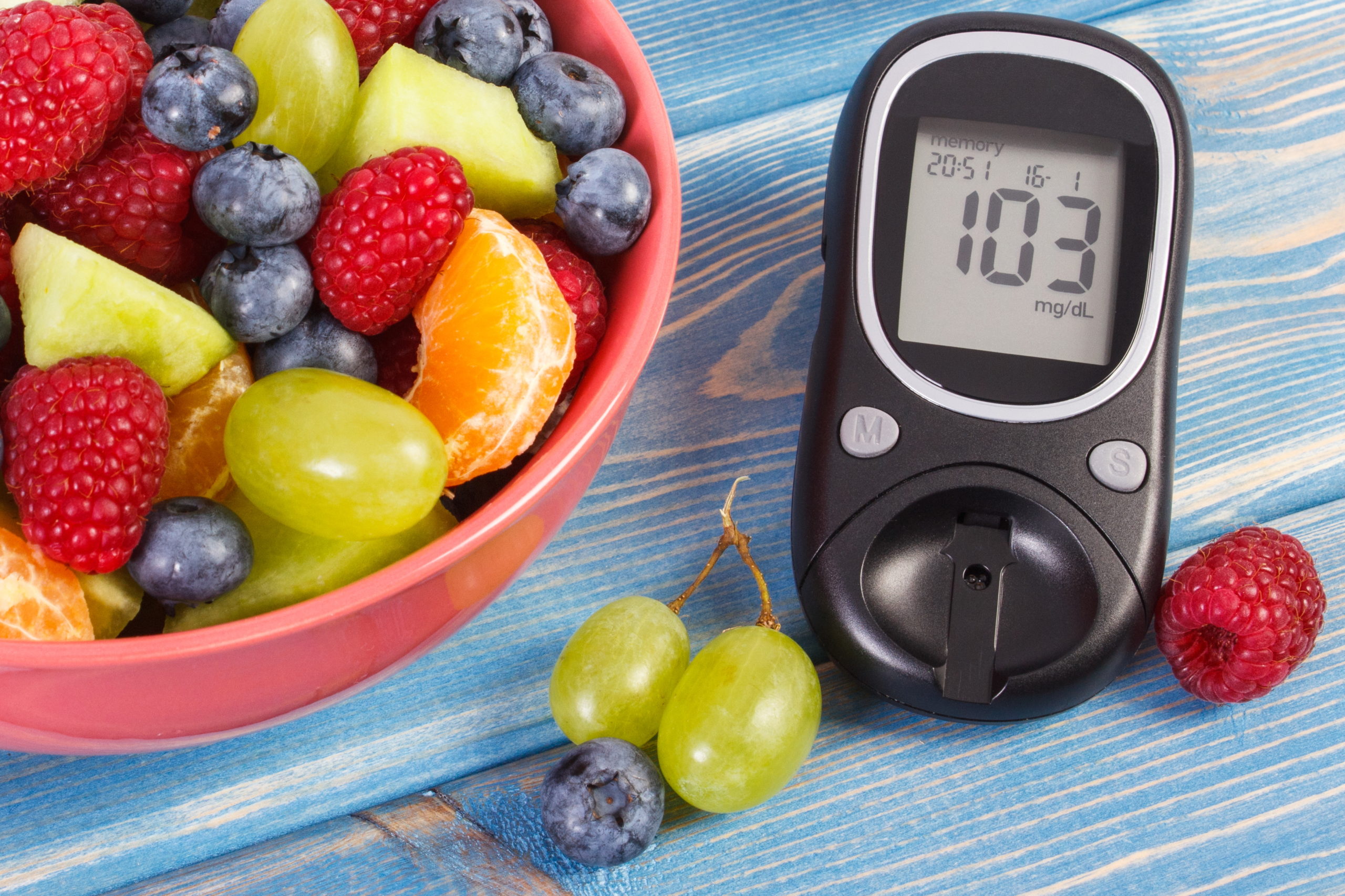
An estimated 30 million Americans have diabetes, a disease in which there is too much sugar in the bloodstream. About 7 million of them, however, have not yet been diagnosed with the disease. Diabetes occurs when the pancreas, a gland behind the stomach, does not produce enough of the hormone insulin, or the body can’t use insulin properly. Insulin helps carry sugar from the bloodstream into the cells. Once inside the cells, sugar is converted into energy for immediate use or stored for the future.
Prediabetes:
Occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. Over time, this can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke, as well as your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Unfortunately, prediabetes symptoms are hard to spot, so many people have the condition and do not know it. Common risk factors include:
Being obese or overweight Not getting enough exercise A family history of type 2 diabetes Being 45 or older Having African-American, Latino/Hispanic or American Indian family background Having had gestational diabetes Giving birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control indicates that about 79 million American adults over the age of 20 have prediabetes. As the population ages, becomes increasingly overweight and increasingly inactive, the number of adults with symptoms of prediabetes continues to grow. The number of young people with this condition is also increasing.
Type 1 Diabetes:
Sometimes called insulin-dependent diabetes and juvenile diabetes, can develop at any age but most often occurs in children, teens, and young adults. In type 1 diabetes, a person’s pancreas produces little or no insulin, so insulin treatment is needed for a lifetime. The causes of type 1 diabetes are not fully known. In most cases, the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the part of the pancreas that produces insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Is the most common form of the disease, affecting 90–95% of people with diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, the body is resistant to the action of insulin, meaning it cannot use insulin properly, so it cannot carry sugar into the cells. Although the body makes some insulin, it is not enough to overcome this resistance. Being older (over 45) and overweight are the greatest risk factors for developing diabetes. Other factors that increase your chances of developing high blood glucose include:


